代码规范
怎样写出更加易懂,易于维护代码
✈️✈️✈️✈️ 用代码讲故事,一个好的故事需要 思想, 修辞,思想是主要内容,要完整的表达出来,修辞 是让思想变的更加通俗易懂
函数
⭐我此时的理解函数,函数是一个y = f(x),对数据进行进行处理转换的过程,有什么样的输入就会有什么样的输出 2023/11/16 /1:42
- 函数的形参数量要少于 3 个,否则可以使用对象形式传递
- 函数无副作用,不影响外部变量
- 函数要么做事,要么回答问题
- 如果无法精确的起一个函数名的话,说明可以再拆分
- 函数要足够单纯,一个函数只做一件事
比如: 添加一个 item
const addItemToCart =(cart,item)=>{
return [...cart,{item}]
}命名
命名要偏向于 🔥函数的功能,而非执行过程
前缀词 + 名词 + 动词 ( is/can/has/ .... + something + verb )
前缀词
- 是否符合状态 -- is
- 能否执行 -- can
- 是否包含 -- has/include/contains
- 是否需要 -- should / need
- 过滤 -- filter filterByName
- 合并 -- merge mergeConfig
- 排序 -- sort sortByAmount
- 转化 -- to toUppderCase / toDollars
- 从对象/数据结构中获取数据 -- get getUserId
- 计算获取数据 -- cal calUserAveragScore
- 分析数据,不能直接获取 -- parse parseUserInfo
- 网络请求 --fetch fetchUserInfo
常量
常量名【应该】使用全部使用大写字母和下划线来组合来命名,下划线用以分割单词;
// 好的常量命名方式
const MAX_IMAGE_SIZE = 10 * 1024 * 1024;
// 不好的常量命名方式
const MaxImageSize = 10 * 1024 * 1024;
const maximagesize = 10 * 1024 * 1024;注释
**声明高层次的意图而非细节。**不要描述显而易见的现象,永远不要用自然语言翻译代码,而应当解释代码为什么要这么做,或者是为了让代码文档化。
不好的
// 这是 Account类 的定义
class Account {
// 给 profile 赋予新的值
setProfile(profile);
}好的
// 权衡图片大小/质量,图片质量设置的最佳值为0.72
image_quality =0.72;在大块长函数前,总结其用途和用法。
使用 // 作为单行注释,【应该】在注释前插入一个空行且使 // 与注释文字之间保留一个空格。
// 不推荐
var active = true; // is current tab
// 推荐
// is current tab
var active = true;使用便于搜索的名称
在代码里搜索数字8是一件很困难的事情,但是如果你搜索常量 MAX_BLOCKS_DISPLAYED 就会简单很多。
if (response.data.user.status === 1) {
// 逻辑处理
} else if (response.data.user.status === 2) {
// 逻辑处理
} else if (response.data.user.status === 3) {
// 逻辑处理
} else {
// 逻辑处理
}
const status = response.data.user.status;
enum STATUS_MAP {
PROCESSING = 1,
ACTICATED = 2,
DISABLED = 3
}
switch (status) {
case STATUS_MAP.PROCESSING:
// 逻辑处理
break;
case STATUS_MAP.ACTICATED:
// 逻辑处理
break;
case STATUS_MAP.DISABLED:
// 逻辑处理
break;
default:
// 逻辑处理
break;
}变量
解释性变量 / 中间变量
一些变量是只在中间使用,但是有实际意义,避免过长的计算过程导致的心智负担
变量名【应该】使用小驼峰式命名法
// 总价格为商品总价(单价 * 数量) - 折扣(超过 100 个打 9 折)
let orderInfo = {
quanity:150,
price:3.7
}
function getTotalPrice (orderInfo) {
// 基础金额
let baseSumMoney = orderInfo.quanity * orderInfo.price;
// 打折金额
let discountMoney = Math.max( 0, orderInfo.quanity - 100 ) * orderInfo.price * 0.1;
return baseSumMoney - discountMoney
}
// 像 baseSumMoney 和 discountMoney 都属于解释型变量遍历中的解释变量
fruits.map(fruit=> doSomeing(fruit))带单位的变量
可以从变量出体现出单位,ts 只能体现出类型
function throttle(
fn:Function,
delay:number // 无法确定 delay 是什么单位
){}通过改变 delaySeconds 可以看出是要传入 seconds 类型
function throttle(
fn:Function,
delaySeconds:number
){}布尔值
使用 is/can/check 前缀词 + 名词 + 形容词/动词
不一定非得包含这三种,主要目的是说明变量的意义
const isDialogOpen = true
const canPageWrite = true
const hasFruit = true数字
一些能够描述数字意义的词语
const minBugs = 1
const maxBugs = 5;
const totalBugs = 3条件语句
使用 switch
function check(){
switch (true) {
case !this.data.info.name:
showToast({ title: ERRORS.NAME });
return;
case (this.data.actived === 2 && this.data.isRawxx.a):
showToast({ title: ERRORS.RECOMMEND });
return;
}
}代码格式
- 应该像读报纸,顶部给出高级的算法和概念,细节依次展开
- 所有的变量统一写到最上面
- 代码组之间添加空白行
(options = arguments[ i ] ) !== null // 赋值判断一起写,好骚
function Clone() {
var clone,copy,
i = 1,
target = arguments[0] || {},
length = arguments.length;
if (typeof target === "boolean") {
target = arguments[1] || {};
}
for (; i < length; i++) {
if((options = arguments[ i ] ) !== null)
for (name in options) {
copy = options[ name ]
if (typeof copy == "object"){
clone = {}
Clone(clone, copy)
} else {
target[ name ] = copy;
}
}
}
return target
}总结: 代码要整洁大气
vue
PascalCase (单词首字母大写命名)是最通用的文件声明约定
kebab-case (短横线分隔命名) 是最通用的使用约定
// 文件命名
MyComponent.vue
// 组件名应该以高级别的 (通常是一般化描述的) 单词开头,以描述性的修饰词结尾
TodoList.vue
TodoListItem.vue
TodoListItemButton.vue
// 基础组件
// 比如 button
BaseButton.vue
BaseTable.vue
// 只应该拥有单个活跃实例的组件应该以 The 前缀命名,以示其唯一性
// 比如 官网的 nav 部分 和 footer 部分 或者 后台管理系统的 侧边栏
TheNav.vue
TheFooter.vue
TheAside.vue<template>
<my-component greeting-text="hi"></my-component>
</template>
<script>
import MyComponent from './MyComponent.vue'
// 可以想象 data-set
props: {
greetingText: String
}
</script>JSDOC
@constant
别名:@const
@constant 标签指明这个对象是一个常量。
/** @constant
@type {string}
@default
*/
const RED = 'FF0000';
/** @constant {number} */
var ONE = 1;@borrows
@borrows标签允许您将另一个标识符的描述添加到你的当前描述。
/**
* @namespace
* @borrows trstr as trim
*/
var util = {
trim: trstr
};
/**
* @param {string} str
*/
function trstr(str) {
return 10
}@description
别名:@desc 如果在注释开始的地方添加描述,那么可省略@description标签。
/**
* Add two numbers.
* @param {number} a
* @param {number} b
* @return {number}
*/
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}@example
中间隔一行
/**
* @example
*
* var object = { 'a': 1 };
* var other = { 'a': 1 };
*
* _.eq(object, object);
* // => true
*
*/@namespace
命名空间
/**
*
* @namespace MyNamespace.
*/
var MyNamespace = {
/**
* A function in MyNamespace (MyNamespace.myFunction).
* @function foo
* @param x {string}
* @memberof MyNamespace
*/
foo: function (x) {},
/**
* @constant
* @type number
* @default 1
*/
bar: 1,
};
MyNamespace.foo;属性
/**
* @namespace
* @property {object} defaults - The default values for parties.
* @property {number} defaults.players - The default number of players.
* @property {string} defaults.level - The default level for the party.
* @property {object} defaults.treasure - The default treasure.
* @property {number} defaults.treasure.gold - How much gold the party starts with.
*/
var config = {
defaults: {
players: 1,
level:'beginner',
treasure: {
gold: 0
}
}
};@param
你可以在变量说明前加个连字符,使之更加容易阅读
/**
* @param {string} somebody - Somebody's name.
*/
function sayHello(somebody) {
alert('Hello ' + somebody);
}普通对象
嵌套的属性名必须使用参数名做为前缀
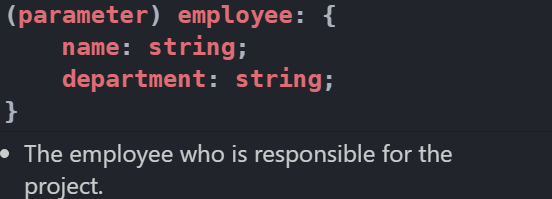
/**
* Assign the project to an employee.
* @param {Object} employee - The employee who is responsible for the project.
* @param {string} employee.name - The name of the employee.
* @param {string} employee.department - The employee's department.
*/
function Project (employee) {
// ...
}
引用其他对象
// 先使用 `typedef`定义 类型
/**
* @typedef {Object} Student - 一个对象
// 描述: 记录一个对象的属性。
* @property {string} name - 一个name
*/
/**
* @type {Student}
*/
let f = {
name:12
}悬浮到 Student 可以直接看到定义
可选参数
/**
* @param {string} [somebody] - Somebody's name.
*/
function sayHello(somebody) {
if (!somebody) {
somebody = 'John Doe';
}
alert('Hello ' + somebody);
}默认参数
/**
* @param {string} [somebody=John Doe] - Somebody's name.
*/
function sayHello(somebody) {
if (!somebody) {
somebody = 'John Doe';
}
alert('Hello ' + somebody);
}多种类型
/**
* @param {(string|string[])} [somebody=John Doe] - Somebody's name, or an
*/
function sayHello(somebody) {
if (!somebody) {
somebody = 'John Doe';
} else if (Array.isArray(somebody)) {
somebody = somebody.join(', ');
}
alert('Hello ' + somebody);
}联合类型
/**
* @param {'GET' | 'POST'} method 请求方法
*/
function m( method ){
}数组对象
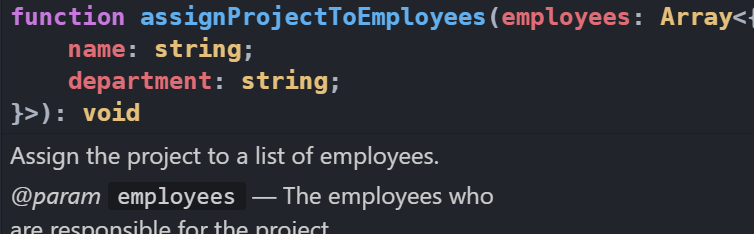
/**
* Assign the project to a list of employees.
* @param {Array.<{ name: string, department: string }>} employees - The employees
*/
function assignProjectToEmployees(employees) {
// ...
}
@callback
/**
* This callback type is called `requestCallback` and is displayed as a global symbol.
*
* @callback requestCallback
* @param {number} responseCode
* @param {string} responseMessage
*/
/**
* Does something asynchronously and executes the callback on completion.
* @param {requestCallback} cb - The callback that handles the response.
*/
function doSomethingAsynchronously(cb) {
// code
};@type
可以使用@type标记并引用一个类型名称
/**@type {string}*/
var s;
/**@type {PromiseLike<string>} */
var promisedString;
// You can specify an HTML Element with DOM properties
/** @type {HTMLElement} */
var myElement = document.querySelector(selector);@type可以指定联合类型—例如,string和boolean类型的联合。
/**
* @type {string | boolean}
*/
var s;有多种方式来指定数组类型:
/** @type {number[]} */
var ns;
/** @type {Array.<number>} */
var nds;
/** @type {Array<number>} */
var nas;指定对象字面量类型
/** @type {{ a: string, b: number }} */
var var9;使用TypeScript或Closure(关闭)语法指定函数类型。
/** @type {function(string, boolean): number} Closure syntax */
var sbn;
/** @type {(s: string, b: boolean) => number} Typescript syntax */
var sbn2;
@type {Function}
var sbn3;@typedef
@typedef可以用来声明复杂类型
/**
* @typedef {Object} SpecialType - creates a new type named 'SpecialType'
* @property {string} prop1 - a string property of SpecialType
* @property {number} prop2 - a number property of SpecialType
* @property {number=} prop3 - an optional number property of SpecialType
* @prop {number} [prop4] - an optional number property of SpecialType
* @prop {number} [prop5=42] - an optional number property of SpecialType with default
*/
/** @type {SpecialType} */
var specialTypeObject;可以直接一行定义
/** @typedef {{ prop1: string, prop2: string, prop3?: number }} SpecialType */
/** @type {SpecialType} */
var specialTypeObject;
/** @typedef {(data: string, index?: number) => boolean} Predicate */
/** @type {Predicate} */
const ok = s => !(s.length % 2);可以跨页面使用,在b.js 可以直接使用 a.js 的定义
/**
* @typedef {(a:number,b:number)=>number} SpecialType
*/
/**
* @type {SpecialType}
*/
function sum(a, b) {
return a + b;
}/**
* @type {SpecialType} SpecialType - some param
*/
function sum2(a, b) {}
sum2(1, 2);@template
使用@template声明泛型
/**
* @template T
* @param {T} x - A generic parameter that flows through to the return type
* @return {T}
*/
function id(x){ return x }
id(1) // 返回的是 number 类型用逗号或多个标记来声明多个类型参数
/**
* @template T,U,V
* @template W,X
*/参数名前指定类型约束
/**
* @template {string} K - K must be a string or string literal
* @template {{ serious(): string }} Seriousalizable - must have a serious method
* @param {K} key
* @param {Seriousalizable} object
*/
function seriousalize(key, object) {
// ????
}
seriousalize("a",{serious:function(){}})@this
编译器通常可以通过上下文来推断出this的类型。但你可以使用@this来明确指定它的类型
/**
* @this {HTMLElement}
* @param {*} e
*/
function callbackForLater(e) {
this.clientHeight = parseInt(e) // should be fine!
}ts中可以使用
/**
*
@description ### 填充模式
- stretch 拉伸充满
- cover 裁切充满,保持图片比例
- contain 全部显示,留白,保持图片比例 */
type mode = "stretch" | "cover" | "contain";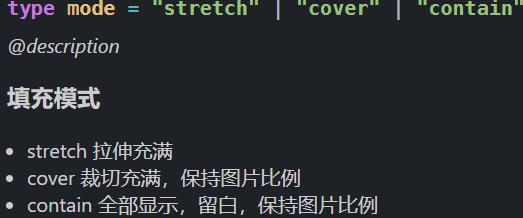
变量提前
我们在执行循环的时候,尽量不要在循环体内创建变量
let sum;
for(let a = 0; a < 10; a++) {
let b = a*2;
sum +=b;
}这每次循环,都创建一个 b
let sum;
let b;
for(let a = 0; a < 10; a++) {
b = a*2;
sum +=b;
}这样的话只会创建一个 b