无限滚动
可以自动执行无限滚动,但是并不是虚拟滚动
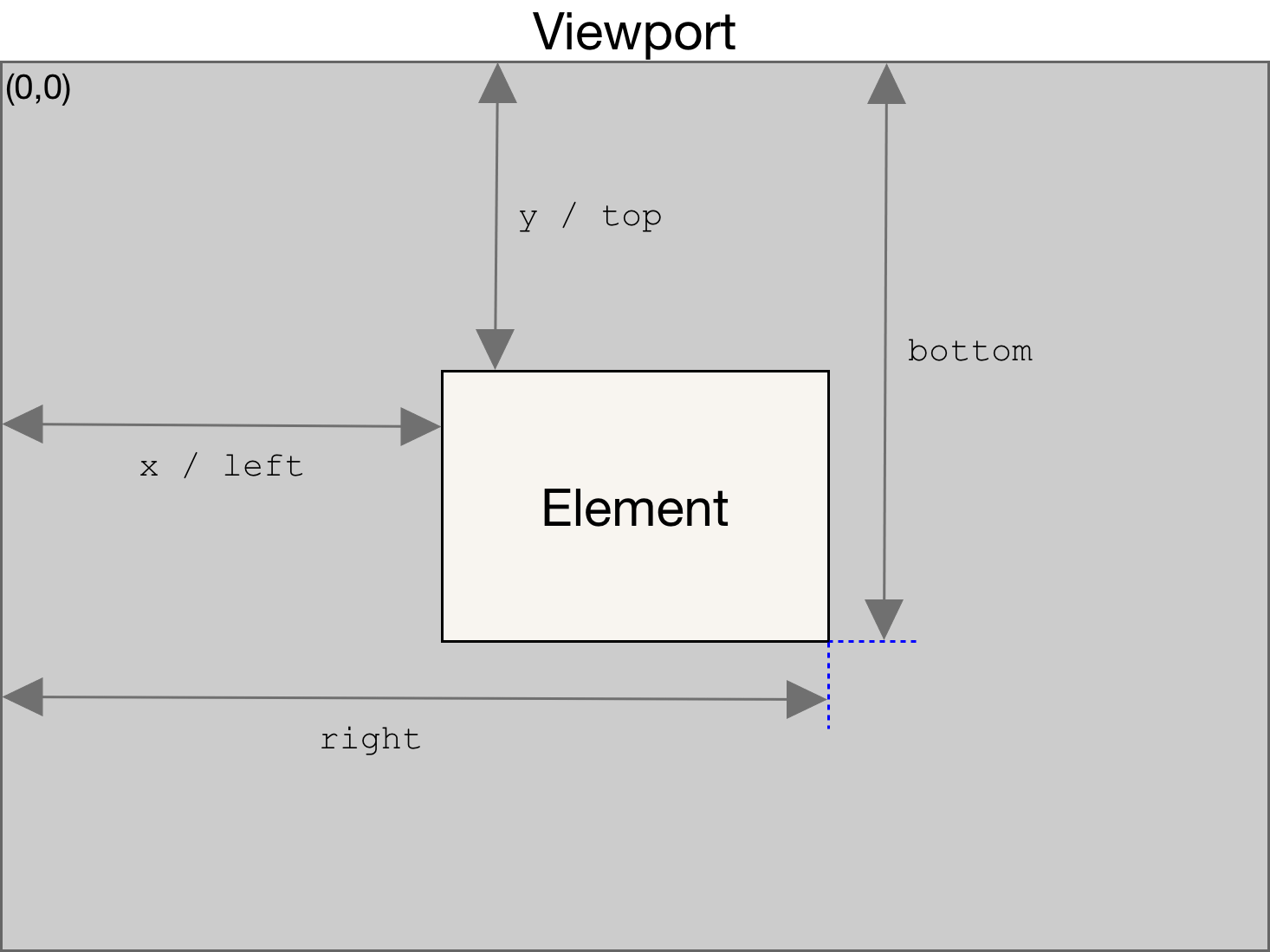
原理
会在最底部设置一个div,然后判断 滚动元素的父元素(container) 的元素的 getBoundingClientRect的bottom 值与 最底部的div 的bottom的差
如果最底部的元素的 bottom 与 container 的 bottom 相等,则说明已经滚动到底部了,然后执行scrollList的loadMore方法,加载数据
效果
核心代码
vue
<template>
<div ref="container" class="h-40 overflow-y-auto ">
<div class="inner" ref="listEl">
<ul>
<li class="p-2 border border-solid border-gray-400 rounded mt-2" v-for="d in info.data">
{{ d }}
</li>
</ul>
<div v-if="info.loading">
<el-icon>
<Loading />
</el-icon>
</div>
<div v-if="info.finished">
<el-icon><CircleCheck /></el-icon>
</div>
<div class="w-full" ref="detectorEl"></div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import { Loading,CircleCheck } from "@element-plus/icons-vue"
import { onMounted, ref, computed, reactive, watch, unref } from "vue";
const container = ref<HTMLElement | null>(null);
const listEl = ref<HTMLElement | null>(null);
const detectorEl = ref<HTMLElement | null>(null);
let scroller: HTMLElement | Window
function getRect(el){
return el.getBoundingClientRect();
}
const isReachBottom = () => {
const { bottom: containerBottom } = getRect(scroller)
// 相对于视口来说
const { bottom: detectorBottom } = getRect(detectorEl.value!)
return detectorBottom <= containerBottom
}
const handleScroll = async () => {
// 找到可以滚动的元素
await nextTick()
if (info.loading || info.finished || !isReachBottom()) {
return
}
load()
}
const getParentScroller = (el: Element) => {
let parent = el.parentElement;
while (parent) {
if (/(auto)|(scroll)/.test(getComputedStyle(parent).overflowY)) {
return parent
}
parent = parent.parentElement;
}
return window
}
onMounted(() => {
scroller = getParentScroller(listEl.value!)
scroller.addEventListener("scroll", handleScroll)
handleScroll()
})
let info = reactive<{
loading: boolean,
finished: boolean,
data: number[]
}>({
loading: false,
finished: false,
data: []
});
const load = function () {
info.loading = true;
setTimeout(() => {
for (let i = 0; i < 60; i++) {
info.data.push(i)
}
info.finished = false
info.loading = false
}, 1000)
}
</script>